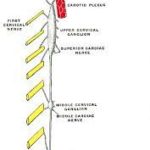
Curcumin prevents neuronal loss and structural changes in the superior cervical (sympathetic) ganglion induced by chronic sleep deprivation, in the rat model
“In modern societies, sleep deprivation is a serious health problem. This problem could be induced by a variety of reasons, including lifestyle habits or neurological disorders. Chronic sleep deprivation (CSD) could have complex biological consequences, such as changes in neural autonomic control, increased oxidative stress, and inflammatory responses. The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is an important sympathetic component of the autonomic nervous system. CSD can lead to a wide range of neurological consequences in SCG, which mainly supply innervations to circadian system and other structures. As the active component of Curcuma longa, curcumin possesses many therapeutic properties; including neuroprotective. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of CSD on the SCG histomorphometrical changes and the protective effect of curcumin in preventing these changes.”
Learn about our two Decals!
 Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.
Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.Berkeley BioDesign Community
 Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.
Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.Search
Student Login




I imagine that the neurological circuits underlying these processes are governed by both 2d spacing maps with their brains as…
to reduce the impact of car accidents, it may be possible to study the force diverting physics of cockroaches to…
you see this type of head-bobbing stability in many avian creatures related to pigeons like chickens. the head ability to…
not like they taught horses how to run! this is an example of convergent evolution where both sea creatures and…
The brain functions in a similar way with neuronal connections. our brains are able to utilize the multiplicity of connections…