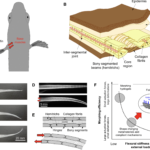
Segmentations in fins enable large morphing amplitudes combined with high flexural stiffness for fish-inspired robotic materials
Fish fins do not contain muscles, yet fish can change their shape with high precision and speed to produce large and complex hydrodynamic forces—a combination of high morphing efficiency and high flexural stiffness that is rare in modern morphing and robotic materials. These “flexo-morphing” capabilities are rare in modern morphing and robotic materials. The thin rays that stiffen the fins and transmit actuation include mineral segments, a prominent feature whose mechanics and function are not fully understood. Here, we use mechanical modeling and mechanical testing on 3D-printed ray models to show that the function of the segmentation is to provide combinations of high flexural stiffness and high morphing amplitude that are critical to the performance of the fins and would not be possible with rays made of a continuous material. Fish fin–inspired designs that combine very soft materials and very stiff segments can provide robotic materials with large morphing amplitudes and strong grasping forces.
Learn about our two Decals!
 Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.
Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.Berkeley BioDesign Community
 Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.
Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.Search
Student Login



I imagine that the neurological circuits underlying these processes are governed by both 2d spacing maps with their brains as…
to reduce the impact of car accidents, it may be possible to study the force diverting physics of cockroaches to…
you see this type of head-bobbing stability in many avian creatures related to pigeons like chickens. the head ability to…
not like they taught horses how to run! this is an example of convergent evolution where both sea creatures and…
The brain functions in a similar way with neuronal connections. our brains are able to utilize the multiplicity of connections…