Paper, Biomimetic design of dorsal fins for AUVs to enhance maneuverability
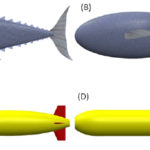
We demonstrate that shape-changing or morphing fins provide a new paradigm for improving the ability of vehicles to maneuver and move rapidly underwater. An ingenious solution is employed by fish to accommodate both the need for stability of locomotion and the ability to perform tight maneuvers: Retractable fins can alter the stability properties of a vehicle to suit their particular goals. Tunas, for example, are large fish that are fast swimmers and yet they need rapid turning agility to track the smaller fish they pursue; they have perfected the use of their dorsal and ventral fins to ensure stability when retracted and rapid turning when erected. Although fish employ unsteady propulsors rather than propellers, we show that engineering rigid-hull underwater vehicles can also exploit similar solutions. We explore the basic flow mechanisms and design considerations of employing morphing fins to alter the stability and maneuvering qualities of vehicles and apply unsteady forces and moments under active control. We also show results from maneuvering simulations and experiments on a model of an underwater vehicle.
Learn about our two Decals!
 Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.
Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.Berkeley BioDesign Community
 Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.
Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.Search
Student Login



I imagine that the neurological circuits underlying these processes are governed by both 2d spacing maps with their brains as…
to reduce the impact of car accidents, it may be possible to study the force diverting physics of cockroaches to…
you see this type of head-bobbing stability in many avian creatures related to pigeons like chickens. the head ability to…
not like they taught horses how to run! this is an example of convergent evolution where both sea creatures and…
The brain functions in a similar way with neuronal connections. our brains are able to utilize the multiplicity of connections…