Paper, Manta Ray Inspired Microplastic Filters
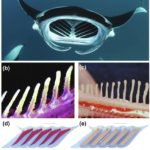
Microplastic particles (MPs) have been identified as a potentially emerging threat to water environment and human health. It is thus an urgent challenge to develop facile and efficient methods for removing MPs from surface water and even ground water. Herein, we report a series of biomimetic gill-inspired membranes (BGIMs) with oblique and direct-through micropores for the efficient removal of MPs by the cross-flowing filtration of polluted water. These BGIMs were constructed via a bidirectional freezing method of thermally induced phase separation. They show a tunable oblique pore angle of 85° to 25° and an average pore size of 3.5 μm to 10.5 μm. MPs smaller than the pore size can be rejected via a ricocheted away mechanism. BGIMs with an oblique pore angle of 25° and an average pore size of 10.5 μm can remove 97.6% of MPs (700 nm in diameter) from water by cross-flowing on the membrane surface with a rate of 0.43 or 0.51 m/s. This effectual removal efficiency highlights BGIMs as a promising approach for quickly remediating water from the pollution of MPs without clogging.
Learn about our two Decals!
 Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.
Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.Berkeley BioDesign Community
 Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.
Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.Search
Student Login



I imagine that the neurological circuits underlying these processes are governed by both 2d spacing maps with their brains as…
to reduce the impact of car accidents, it may be possible to study the force diverting physics of cockroaches to…
you see this type of head-bobbing stability in many avian creatures related to pigeons like chickens. the head ability to…
not like they taught horses how to run! this is an example of convergent evolution where both sea creatures and…
The brain functions in a similar way with neuronal connections. our brains are able to utilize the multiplicity of connections…