Paper, Sharkskin inspired antibacterial surface
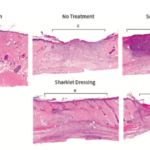
Nearly 12 million wounds are treated in emergency departments throughout the United States every year. The limitations of current treatments for complex, full-thickness wounds are the driving force for the development of new wound treatment devices that result in faster healing of both dermal and epidermal tissue. Here, a bilayered, biodegradable hydrogel dressing that uses microarchitecture to guide two key steps in the proliferative phase of wound healing, re-epithelialization, and revascularization, was evaluated in vitro in a cell migration assay and in vivo in a bipedicle ischemic rat wound model. Results indicate that the SharkletTM-micropatterned apical layer of the dressing increased artificial wound coverage by up to 64%, P 1⁄4 0.024 in vitro. In vivo evaluation demonstrated that the bilayered dressing construction enhanced overall healing outcomes significantly compared to untreated wounds and that these outcomes were not significantly different from a leading clinically available wound dressing. Collectively, these results demonstrate high potential for this new dressing to effectively accelerate wound healing.
Learn about our two Decals!
 Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.
Click here to find out more about our Fall Bioinspired Design Decal and our Spring Bioinspired Design in Action Decal – ALL MAJORS are welcome.Berkeley BioDesign Community
 Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.
Click here to learn about the BioD: Bio-Inspired Design @ Berkeley student organization or here to signup for more info.Search
Student Login




I imagine that the neurological circuits underlying these processes are governed by both 2d spacing maps with their brains as…
to reduce the impact of car accidents, it may be possible to study the force diverting physics of cockroaches to…
you see this type of head-bobbing stability in many avian creatures related to pigeons like chickens. the head ability to…
not like they taught horses how to run! this is an example of convergent evolution where both sea creatures and…
The brain functions in a similar way with neuronal connections. our brains are able to utilize the multiplicity of connections…